Core 3
Functions
A function is a one to one mapping
Domain and range of a function
The domain of a function is the set of valid input values
A function is defined by both a rule and a domain
Inverse of a function
An inverse function is such that
For a function to have a valid inverse function, it must be a one to one mapping
Transformations and the modulus function
Translations
Translating the function by the vector gives
is a stretch of by a factor of in the direction
is a stretch y a factor of in the direction
Reflecting in the y axis gives
The modulus of a function is given by:
Inverse trigonometric functions
has domain and range of
has domain and range of
has domain and range of
Trig identities
Calculus
Log rules
Differentials and integrals
The chain rule
The product rule
or
The quotient rule
or
Integration by inspection and substitution
Integration by parts and standard integrals
More simply
In general it is easier to make the simpler part of the given integrand.
Volume of a revolution
The volume of a function rotated fully around the axis is given by
To find the volume of a revolution around the axis, rearrange the function to the form .
Numerical solutions and iterative methods
Iteration
Iteration requires a formula in the form
An iterative formula converges if | for certain values of x
If the iteration converges to a limit the limit can be found by setting
Trapezium rule
If tends upwards the rule will overestimate, and if tends downwards the rule will underestimate.
Mid-Ordinate rule
Where is even.
Simpson’s rule
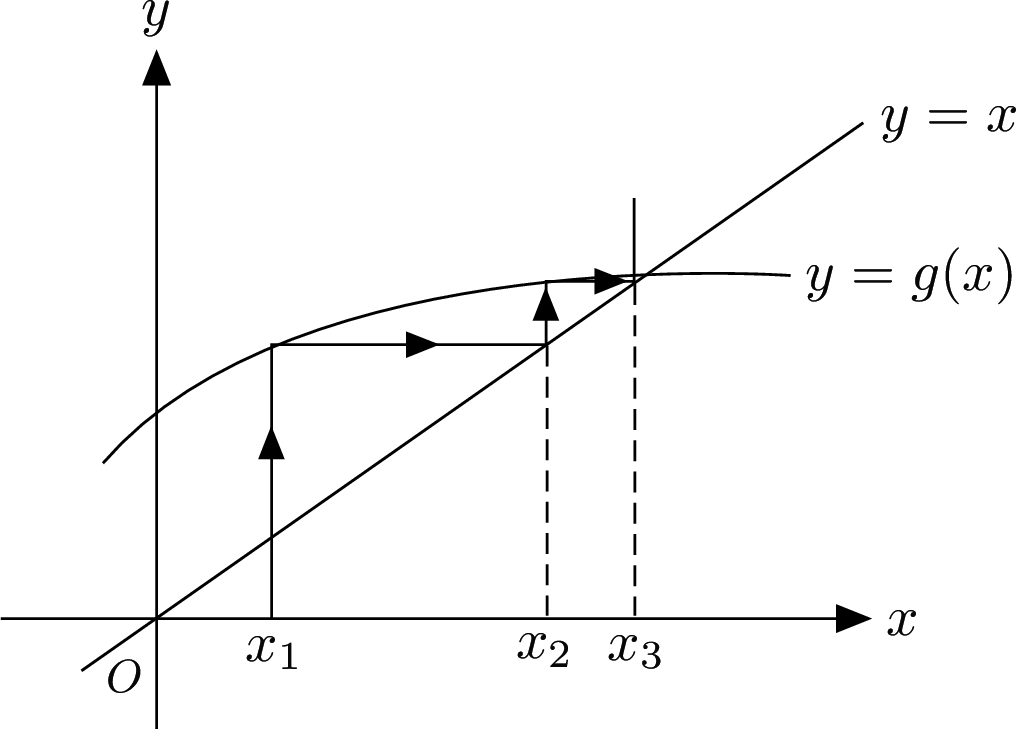
Cobweb diagram
Plot the two functions
A cobweb diagram is plotted by drawing up from the first x value, before rotating around, alternating between each of the functions for each value of x.
This is more appropriate when the values converge around the root rather than towards it.
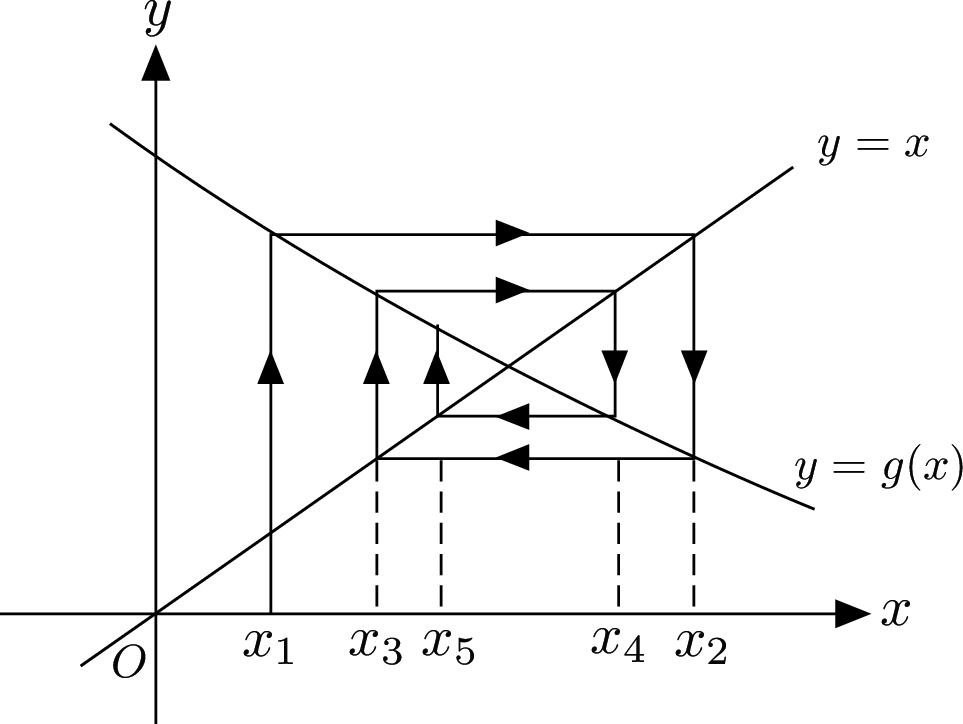
Staircase diagram
Plot the two functions
A staircase is plotted by drawing a line up from each x value to one of the functions, and then drawing across to the next intersect with the other function.